Anna de Vries - Sunne Tech
Light-driven CO2 capture as low-cost and geographically flexible carbon removal technology.
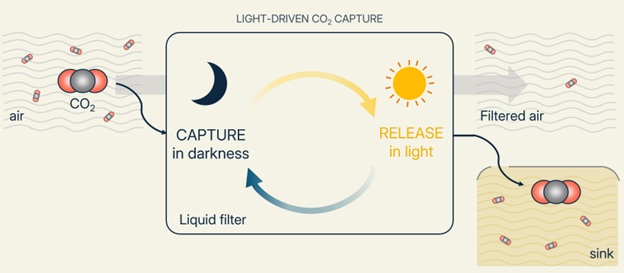
Reducing atmospheric CO2 requires both emission cuts and technologies that physically remove CO2 from industrial streams and air itself. CO2 can be removed from industrial flue gases via carbon capture, or extracted from ambient air via Direct Air Capture (DAC) – both quantifiable and immediate approaches to lowering atmospheric CO2 levels. Existing carbon capture and direct air capture technologies rely on renewable heat or electricity, which is not always abundantly available. In search of minimizing and diversifying the renewable energy demand for CO2 capture, we are developing a novel light-driven approach. In our “Sun-driven Negative Emission” (SUNNE) Technology, sunlight serves as the driving force for the CO2 capture process. The process follows the same two-step principle as traditional CO2 capture, but instead of relying on heat or electricity, this process is driven by exposure to sunlight. The project is running in the Electrochemical Energy Systems Laboratory at ETH Zurich, led by Prof. Maria Lukatskaya and Anna de Vries. With the support of the Pioneer Fellowship, we are advancing from bench-scale research to practical implementation. Our objective is to unlock scalable carbon removal by harnessing sunlight directly, advancing toward a net-zero carbon economy.
